Details
-
Bug
-
Status: Resolved
-
Critical
-
Resolution: Fixed
-
1.1.0
-
None
Description
While running iterative algorithms in GraphX, a StackOverflow error will stably occur in the serialization phase at about 300th iteration. In general, these kinds of algorithms have two things in common:
- They have a long computing chain.
(e.g., “degreeGraph=>subGraph=>degreeGraph=>subGraph=>…=>”)
- They will iterate many times to converge. An example:
//K-Core Algorithm val kNum = 5 var degreeGraph = graph.outerJoinVertices(graph.degrees) { (vid, vd, degree) => degree.getOrElse(0) }.cache() do { val subGraph = degreeGraph.subgraph( vpred = (vid, degree) => degree >= KNum ).cache() val newDegreeGraph = subGraph.degrees degreeGraph = subGraph.outerJoinVertices(newDegreeGraph) { (vid, vd, degree) => degree.getOrElse(0) }.cache() isConverged = check(degreeGraph) } while(isConverged == false)
After about 300 iterations, StackOverflow will definitely occur with the following stack trace:
Exception in thread "main" org.apache.spark.SparkException: Job aborted due to stage failure: Task serialization failed: java.lang.StackOverflowError
java.io.ObjectOutputStream.writeNonProxyDesc(ObjectOutputStream.java:1275)
java.io.ObjectOutputStream.writeClassDesc(ObjectOutputStream.java:1230)
java.io.ObjectOutputStream.writeOrdinaryObject(ObjectOutputStream.java:1426)
java.io.ObjectOutputStream.writeObject0(ObjectOutputStream.java:1177)
It is a very tricky bug, which only occurs with enough iterations. Since it took us a long time to find out its causes, we will detail the causes in the following 3 paragraphs.
Phase 1: Try using checkpoint() to shorten the lineage
It's easy to come to the thought that the long lineage may be the cause. For some RDDs, their lineages may grow with the iterations. Also, for some magical references, their lineage lengths never decrease and finally become very long. As a result, the call stack of task's serialization()/deserialization() method will be very long too, which finally exhausts the whole JVM stack.
In deed, the lineage of some RDDs (e.g., EdgeRDD.partitionsRDD) increases 3 OneToOne dependencies in each iteration in the above example. Lineage length refers to the maximum length of OneToOne dependencies (e.g., from the finalRDD to the ShuffledRDD) in each stage.
To shorten the lineage, a checkpoint() is performed every N (e.g., 10) iterations. Then, the lineage will drop down when it reaches a certain length (e.g., 33).
However, StackOverflow error still occurs after 300+ iterations!
Phase 2: Abnormal f closure function leads to a unbreakable serialization chain
After a long-time debug, we found that an abnormal f function closure and a potential bug in GraphX (will be detailed in Phase 3) are the "Suspect Zero". They together build another serialization chain that can bypass the broken lineage cut by checkpoint() (as shown in Figure 1). In other words, the serialization chain can be as long as the original lineage before checkpoint().
Figure 1 shows how the unbreakable serialization chain is generated. Yes, the OneToOneDep can be cut off by checkpoint(). However, the serialization chain can still access the previous RDDs through the (1)->(2) reference chain. As a result, the checkpoint() action is meaningless and the lineage is as long as that before.
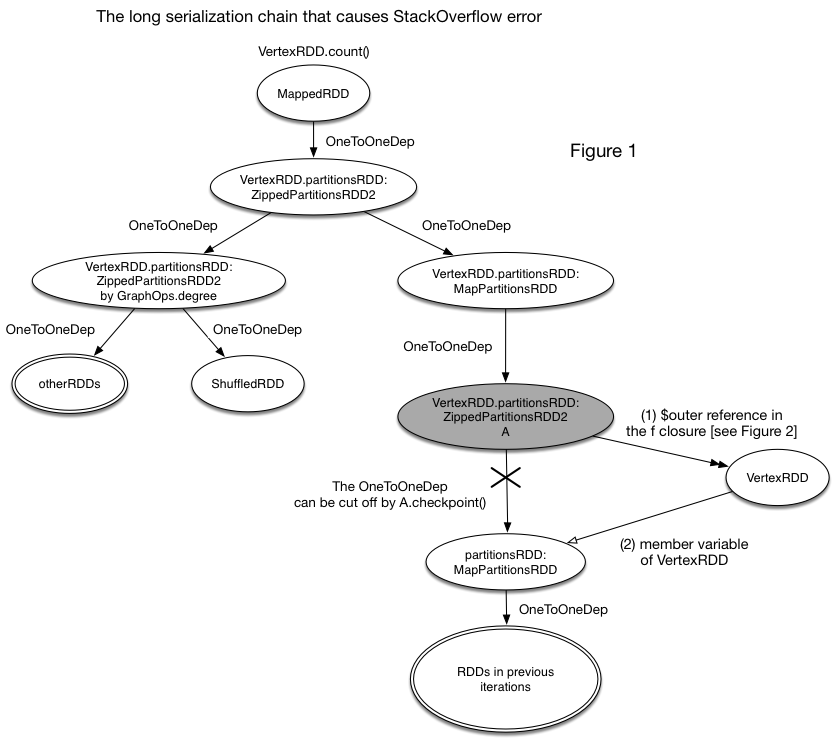
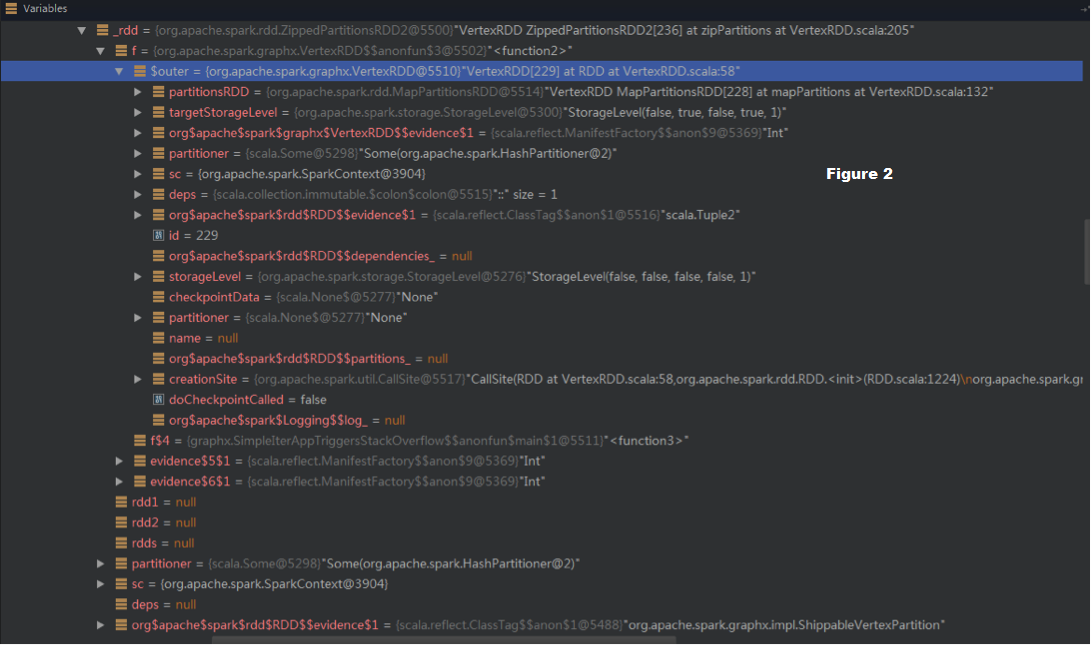
The (1)->(2) chain can be observed in the debug view (in Figure 2).
_rdd (i.e., A in Figure 1, checkpointed) -> f -> $outer (VertexRDD) -> partitionsRDD:MapPartitionsRDD -> RDDs in the previous iterations
More description: While a RDD is being serialized, its f function
e.g., f: (Iterator[A], Iterator[B]) => Iterator[V]) in ZippedPartitionsRDD2
will be serialized too. This action will be very dangerous if the f closure has a member “$outer” that references its outer class (as shown in Figure 1). This reference will be another way (except the OneToOneDependency) that a RDD (e.g., PartitionsRDD) can reference the other RDDs (e.g., VertexRDD). Note that checkpoint() only cuts off the direct lineage, while the function reference is still kept. So, serialization() can still access the other RDDs along the f references.
Phase 3: Non-transient member variable of VertexRDD makes things worse
"Reference (1)" in Figure 1 is caused by the abnormal f clousre, while "Reference (2)" is caused by the potential bug in GraphX: PartitionsRDD is a non-transient member variable of VertexRDD.
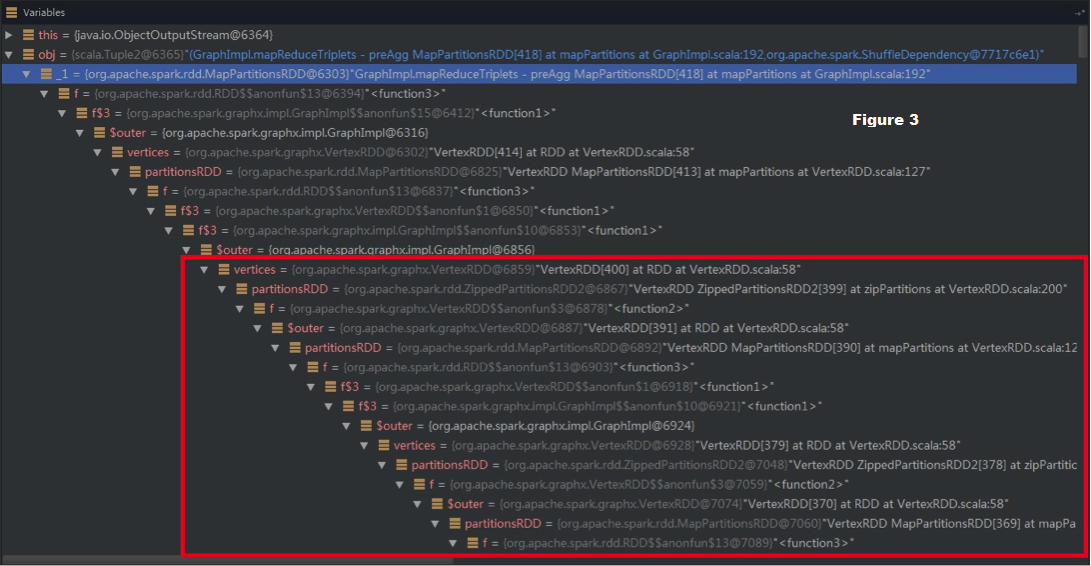
With this small bug, the f closure itself (without OneToOne dependency) can cause StackOverflow error, as shown in the red box in Figure 3:
- While vertices:VertexRDD is being serialized, its member PartitionsRDD will be serialized too.
- Next, while serializing this partitionsRDD, serialization() will simultaneously serialize its f’s referenced $outer. Here, it is another partitionsRDD.
- Finally, the chain
"f => f$3 => f$3 => $outer => vertices: VertexRDD => partitionsRDD => … => ShuffledRDD"
comes into shape. As a result, the serialization chain can be as long as the original lineage and finally triggers StackOverflow error.
Conclusions
In conclusion, the root cause of StackOverflow error is the long serialization chain, which cannot be cut off by checkpoint(). This long chain is caused by the multiple factors, including:
- long lineage
- $outer reference in the f closure
- non-transient member variable
How to fix this error
We propose three pull requests as follows to solve this problem thoroughly.
- PR-3544
In this pr, we change the "val PartitionsRDD" to be transient in EdgeRDDImpl and VertexRDDImpl. As a result, while vertices:VertexRDD is being serialized, its member PartitionsRDD will not be serialized. In other words, the "Reference (2)" in Figure 1 will be cut off. - PR-3545
In this pr, we set "f = null" if ZippedPartitionsRDD is checkpointed. As a result, when PartitionsRDD is checkpointed, its f closure will be cleared and the "Reference (1)" (i.e., f => $outer) in Figure 1 will no exist. - PR-3549
To cut off the long lineage, we need to perform checkpoint() on PartitionsRDD. However, current checkpoint() is performed on VertexRDD and EdgeRDD themselves. As a result, we need to override the checkpoint() methods in VertexRDDImpl and EdgeRDDImpl to perform checkpoint() on PartitionsRDD.
Attachments
Issue Links
- relates to
-
SPARK-3623 Graph should support the checkpoint operation
-
- Resolved
-
- links to